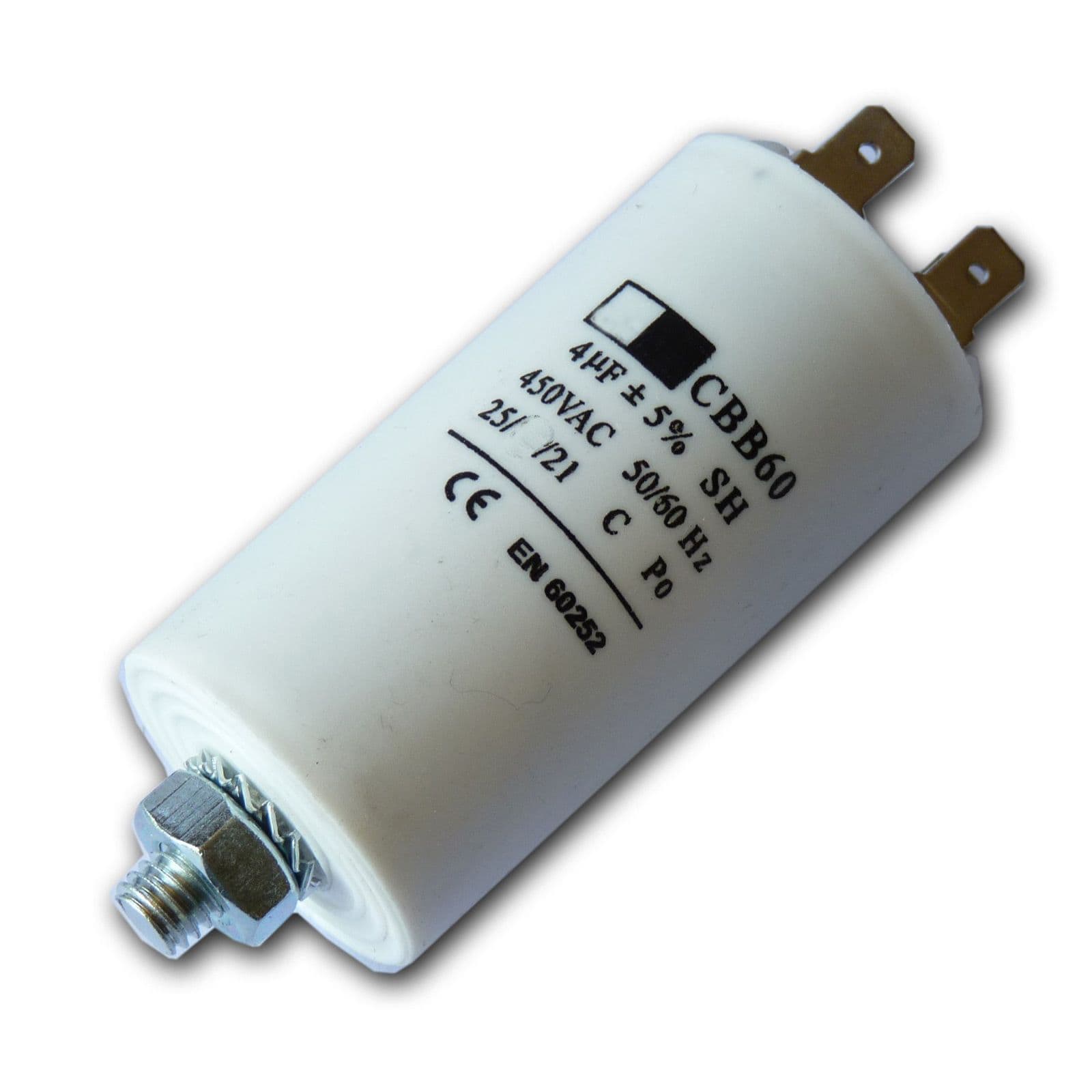
Capacitors are essential components in various electronic devices, enabling the storage and release of electrical energy. Have you ever wondered how these small but mighty devices are made? In this article, we will delve into the intricate process of manufacturing capacitors, exploring the materials, techniques, and quality control measures involved.
- Selection of Capacitor Type:
There are numerous types of capacitors available, each designed for specific applications. Manufacturers carefully consider factors such as capacitance, voltage rating, temperature stability, and size requirements to determine the most suitable type for a particular application. - Materials Used:
Capacitors consist of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. The choice of materials greatly impacts the performance and reliability of the capacitor. Common materials include aluminum, tantalum, ceramic, polyester, and polypropylene. Each material possesses unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications. - Manufacturing Techniques:
a. Electrolytic Capacitors:
- Anodization: For aluminum electrolytic capacitors, the aluminum foil is anodized to form a thin oxide layer, which acts as the dielectric.
- Electrolyte Filling: The anodized foil is then immersed in an electrolyte solution, allowing it to absorb the electrolyte and enhance the capacitance.
- Sealing: The electrolyte-filled foil is sealed in a casing, ensuring airtightness and preventing leakage.
b. Ceramic Capacitors:
- Ceramic Powder Preparation: Ceramic powder is mixed with additives to achieve the desired dielectric properties.
- Forming: The mixture is shaped into discs or other desired forms, which are then sintered at high temperatures to create a solid ceramic structure.
- Electrode Application: Conductive materials are applied to the ceramic structure to form the plates.
- Stacking and Encapsulation: Multiple ceramic layers with electrodes are stacked and encapsulated to form a compact capacitor.
c. Film Capacitors:
- Film Production: Thin films of dielectric materials, such as polyester or polypropylene, are produced using techniques like extrusion or vacuum deposition.
- Electrode Deposition: Conductive metal layers, typically aluminum or zinc, are deposited onto the dielectric films.
- Winding or Stacking: The dielectric films with electrodes are either wound into a cylindrical shape or stacked to form a compact capacitor.
- Encapsulation: The wound or stacked capacitor is encapsulated to protect it from external influences.
- Quality Control:
Manufacturers implement stringent quality control measures to ensure the reliability and performance of capacitors. These include:
- Testing capacitance, voltage rating, and temperature stability.
- Checking for any defects or irregularities in the materials or manufacturing process.
- Conducting environmental tests to assess the capacitors' resistance to temperature, humidity, and mechanical stress.
- Sampling and batch testing to ensure consistency and reliability.
Conclusion:
The manufacturing process of capacitors involves a combination of precise techniques, careful material selection, and rigorous quality control measures. Understanding how capacitors are made provides valuable insights into their functionality and reliability. As these essential components continue to advance, manufacturers strive to improve efficiency, increase capacitance, and enhance overall performance, contributing to the ever-evolving world of electronics.